The notes are summary for the course Reinforcement Learning at University Stuttgart in SS23.
Characteristics of reinforcement learning
- no supervisor, only a reward signal
- Feedback is (often) delayed, non instantaneous -
- Time really matters (sequential, non i.i.d data)
- Agent’s actions affect the subsequent data it receives
Exploitation vs. exploration
在强化学习中,利用已知信息以获取当前最大回报的策略称为利用(exploitation),而在不确定性较高的情况下尝试新的策略来探索更多可能的回报称为探索(exploration)。利用能够尽快获取最大回报,但可能会错过更高的回报,探索能够寻找到更高的回报,但需要付出更多的时间和资源。在选择策略时需要平衡利用和探索之间的关系。
- Exploration: finds more information about the environment
- Exploitation: exploits known information to maximise reward
- Too much exploration could waste resources, too much exploitation could limit learning an lead to a suboptimal results.
- give 2 examples for them:
- Dining: go to your favourite restaurant vs. try something new
- Advertisment: place a new advert vs. the most relevant
Estimating action-values
Sample average method:
在强化学习中,Sample Average Method(样本平均法)是一种估计动作值函数的方法。它通过计算动作的平均奖励来估计动作的价值。在这种方法中,每次选择某个动作后,将其奖励值加入该动作的历史奖励值中,并将结果除以该动作被选择的次数来计算其平均奖励值。由于在每个时间步上都会更新所有动作的值,因此Sample Average Method通常用于非常小的动作空间。相对于其他估计动作值函数的方法,如TD-learning和Q-learning,样本平均法的收敛速度较慢,但是对于某些问题来说,仍然是一种有效的方法。
- What is the difference between
and is the true value of a is the value of greedy action at time t
这只是估计action value的一种很直接的方式, 但不一定是最佳的方式。这种方式直接基于历史的奖励值来估计其动作的价值。
Action selction
在得到 action-state function
- With probability
take the greedy action (exploitation) - With probability
take the random action (exploration) - This selection method prefer to choose exploitation action, so it calls
-greedy action selection.
Epsilon-Greedy行动选择是一种在强化学习中平衡探索和利用之间的策略。该策略在选择下一步行动时,以概率1-ε(其中ε是小于1的正数)选择当前最优的行动(利用),以概率ε选择随机的行动(探索)。这样可以尽可能地利用已知的最优策略,同时也允许一定的探索空间,以便在未知情况下尝试新的行动。通过调整ε的大小,可以控制利用和探索之间的权衡,以适应不同的学习环境
Definition: This is a simple idea to force continued exploration. The Algorithm will take the greedy action with probability
For epsilon greedy and greedy method, which one is better in each of these cases?
- What if reward variance is very small, e.g. zero? choose greedy method
- If the variance in reward is very small or zero, this indicates that the environment is deterministic. In this case, a greedy method might perform better because once the agent has learned the optimal action, there's no benefit from further exploration. Since the rewards for each action don't vary, the agent can quickly learn the best action and always select it.
- What if reward variance is larger? choose
- greedy method - When there's a larger variance in reward, the epsilon-greedy method could be a better choice. In environments with high variance, a single action might sometimes yield a high reward and sometimes a low reward. The epsilon-greedy strategy's occasional exploration can help confirm or update the agent's knowledge about the value of each action.
- What if task is non-stationary? choose
- greedy method - For non-stationary tasks, where the environment and the associated rewards can change over time, an epsilon-greedy approach would likely perform better. This is because constant exploration (which epsilon-greedy provides) allows the agent to keep learning about the environment and adapt to changes. The greedy method might fail to adapt in this case because it tends to stick with the action that was optimal in the past.
Softmax action selection
- Why we need softmax action selection?
- Because the worst action has same probability as second-best action.
具体来说,Softmax action selection使用softmax函数将每个行动的预测值转换为概率,然后基于这些概率进行随机选择。softmax函数的作用是将任何一组实数转换为介于0和1之间的概率分布,它的输出值是一个概率向量,其中每个元素都是介于0和1之间的数字,这些数字的总和为1。
在强化学习中,softmax函数通常用于将Q值(行动价值函数)转换为概率。具体来说,对于给定的状态,假设每个行动的Q值分别为
这样的好处是如果只用Sample average method计算的Q值, 如果Q之间的值差别特别大的时候,也就是动作空间非常大,不同的action造成的后果差别非常大,因此用softmax将动作空间归一化,以提高准确度。
Effect of temperature:
- why we need hyperparameter temperature in softmax?
- It's used to keep balance between exploitation and exploration.
- as
, high temperature, the softmax function provides a uniform distribution, which means every action has the same probability causing the agent to explore the environment more. - as
, low temperature, softmax function provides a distribution which focus on the action with highest value. This encourages exploitation rather than exploration.
Incremental action-value estimates
- Why we need incremental action-value estimates?
- Because this method requires less memory and computation complexity.
- Running time is
- Running time is
- For the original formula to compute action-value, the memory and computational requirement will grow over time. Each additional reward would require additional memory to store it and additional computation to compute the sum in the numerator.
- Running time is
有别于Sample average method,incremental 只计算增量,类似于迭代的过程,会大大降低复杂度.
- Running time is
- Because this method requires less memory and computation complexity.
This makes it a very efficient method for reinforcement learning, particularly in environments with large state and action spaces.
Stepsize depends on
- What is the implication of keeping α constant?
- gives more weights to recent rewards
- consider non-stationary environments, the constant stepsize allow the agent focus on the most recent trends.
Exercise

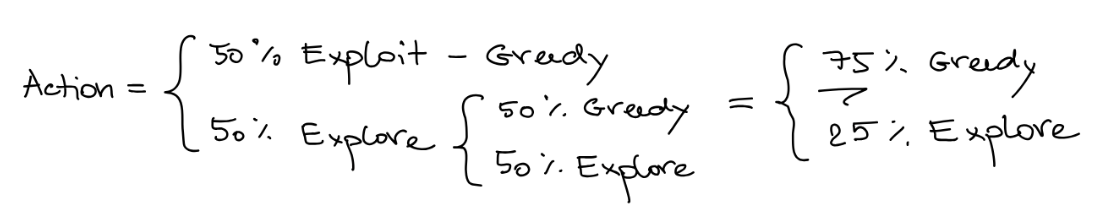



Winner would be red one (ε = 0.01) because it converges to 1 - ε = 0.99. It is 0.09 greater than blue one (ε = 0.1) which converges to 1 - ε = 0.9.

